Data Center
In the rapidly evolving landscape of data centers, the demand for high-speed, reliable, and efficient data transmission has never been greater. Fiber optic communication products have emerged as the backbone of modern data centers, offering unparalleled performance and scalability.
At present, the internal communication of the data center accounts for the vast majority of the communication of the data center, and the great development of the construction of the data center has promoted the development of high-speed optical modules, and the application prospects of high-speed optical modules are getting better and better.
5G Network
The 5G bearer network realizes the fronthaul, midhaul and backhaul functions of 5G services through the metropolitan area network and the backbone network, in which the devices at each layer mainly rely on optical fibers and optical modules to achieve interconnection. Different types of transceivers are required for different solutions.
5G communication optical modules can be divided into SFP28/QSFP28 and other packaging forms according to the different packaging of optical modules, according to the different functions of optical modules, they can be divided into transmitting modules, receiving modules and transceiver modules, and according to the different rates of optical modules, they can be divided into 25G, 50G, 100G, 200G and 400G optical modules.
Metro Network

Optical fiber communication plays an important role in metropolitan area networks. It connects local area networks and data centers within the city, building the main artery of information transmission. Optical fiber technology supports high-speed and large-capacity transmission, helping the development of smart cities.
CWDM technology and DWDM technology effectively enhance transmission efficiency and capacity, and are widely used in metropolitan area networks with ultra-large capacity data transmission.
With the emergence of emerging technologies such as the Internet of Things, big data, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence, the demand for optical fiber communication is growing. In the future, optical fiber communication technology will continue to evolve in the direction of ultra-large capacity, intelligence, and integration, realizing intelligent network parameter monitoring and ultra-long distance and ultra-large capacity information transmission.
Access Network
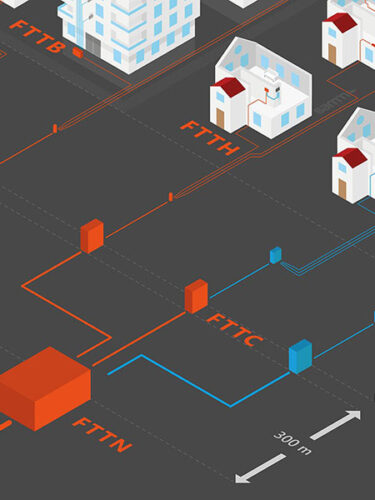
The FTTX broadband optical access network uses optical fiber media to replace part or all of the traditional metal wire media, extends the optical fiber from the central office to the user end, and deploys the ONU to the flexible point (FP) and distribution point (DP) of the traditional access network, and finally reaches the user equipment or user network. In the process of broadband and optical fiberization, the FTTX access network is affected by the service requirements of the customer group, the network resources of operators, the service types, functions and performance supported by various bearer technologies on the optical fiber, and the evolution strategy, so that the broadband optical access network has different application models according to the location of the ONU, such as FTTCab, FTTB, FTTC, FTTH, etc. FTTX is a collective term for the various application types of broadband optical access networks mentioned above, and there are many variants of “X”, which can be fiber-to-the-building (FTTB), fiber-to-the-box (FTTCab), fiber-to-the-curbside (FTTC), fiber-to-the-desk (FTTD), fiber-to-the-home (FTTH), fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP), fiber-to-the-office (FTTO), fiber-to-the-customer (FTTu), etc.



